The Evolving Landscape of Chinese Medicine Research
Chinese mainland remains the primary research powerhouse in Chinese Medicine research, the involvement of international partners, particularly through hubs like Hong Kong SAR (China), has been instrumental in enhancing the field’s global visibility and impact.
Research in Chinese Medicine has demonstrated remarkable growth over the past decade (2014–2023), with annual publication output nearly tripled from 2014 to 2022.
The yearly research output in the field of Chinese Medicine increased continually, from below 13,000 publications in 2014 to more than 32,000 in 2022. This growth outpaced the global research average, showing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6% compared to 3.9% for overall global research output.
Overview of global research output in the field of Chinese Medicine, 2014–2023
The quality and impact of Chinese Medicine research have been impressive.
14.2% of publications in the field rank in the top 10% most cited publications globally, exceeding the expected global average of 10%.
The share of the top 10% most cited publications increased from 13.7% for the period of 2014-2018 to 14.4% in the recent five years between 2019 and 2023.
Overview and five-year comparison of the global top 10% highly cited research output in the field of Chinese Medicine, 2014–2023
The field-weighted citation impact (FWCI) of 1.12 for the entire period indicates that Chinese Medicine research has been cited 12% more than the global average, with this metric improving from 1.05 in 2014–2018 to 1.16 in 2019–2023.
Overview and five-year comparison of FWCI for the research output of Chinese Medicine published in 2014–2018 and 2019–2023
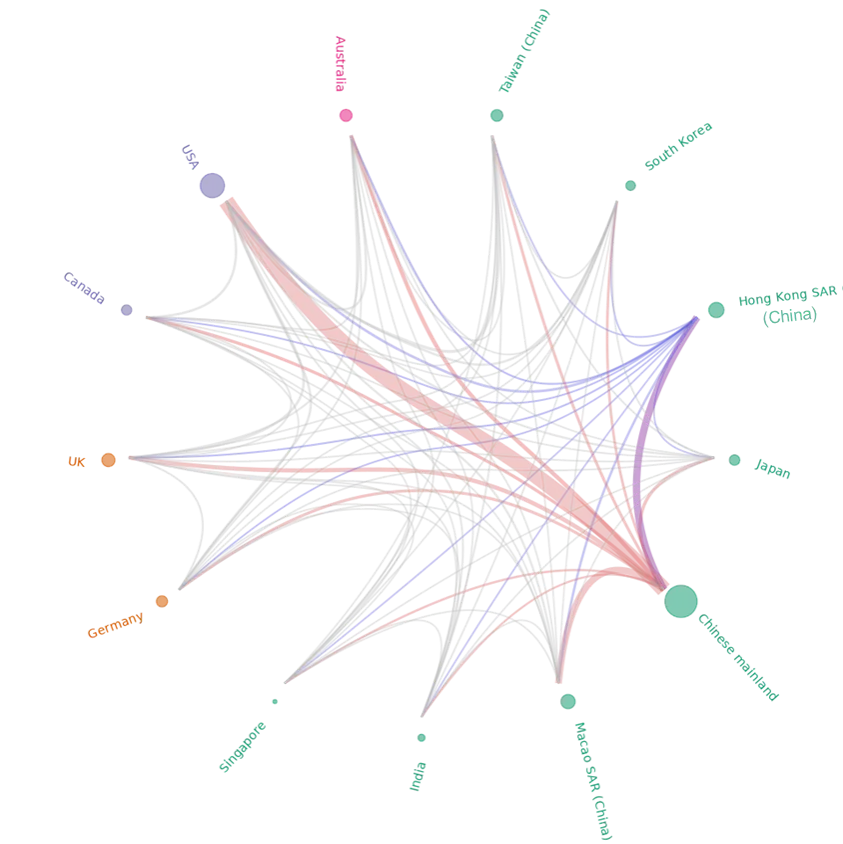
The patterns of the dynamic collaboration networks illustrate the strategic positioning of regions such as Hong Kong SAR (China) and the Chinese mainland within the broader scientific landscape.
Hong Kong SAR (China) and Macao SAR (China) have distinguished themselves as important hubs for regional collaboration in Chinese Medicine research.
Over 80% of their research output involves cross-regional partnerships —significantly above the global average of 18.1%. Their collaborative research consistently achieves high citation impact, with FWCI exceeding 1.6.
International & regional collaboration performance for the most published countries/regions, 2014–2023
Hong Kong SAR (China) and Macao SAR (China) have shown steady increases in the share of internationally and regionally collaborative output.
This underscores that Hong Kong and Macao have become increasingly active in cross-geographic collaborations.
International & regional collaboration trend of share for the most published countries/regions, 2014–2023
A deep dive into the collaboration network for Chinese mainland and Hong Kong SAR (China) reveals significant regional partnerships in Chinese Medicine research and development.
The collaboration network of Hong Kong SAR (China) is particularly impressive, with partnerships generating exceptionally high citation impact.
Hong Kong SAR (China)’s collaboration networks highlight its close connection to the Chinese mainland, USA stands out as the second largest partner for Hong Kong SAR (China), with 732 co-authored publications and a high FWCI of 2.37, suggesting impactful research stemming from the collaboration, despite a relatively small output volume.
Collaboration network for the Chinese mainland and Hong Kong SAR (China), 2014–2023